Plots of r⁴ vs. t (a) and r² vs. t (b) of Laves phases at two
4.8 (112) · $ 4.99 · In stock
Download scientific diagram | Plots of r⁴ vs. t (a) and r² vs. t (b) of Laves phases at two formation paths (Laves phase next to M23C6 and isolated Laves phase) during creep process. Note that the fitting parameters R² are also given. from publication: Creep-induced heterogeneous precipitation of Laves phase with two morphologies in tempered martensite ferritic steels | We report two typical morphologies (elongated- and blocky-shaped) of the Laves phase in tempered martensite ferritic steels during creep process, originating from the two independent formation paths, i.e. along grain boundaries (GBs) and neighboring M23C6. This is attributed | Martensite, Ferrites and Temperance | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Competition between solid solution and multi-component Laves phase in a dual-phase refractory high-entropy alloy CrHfNbTaTi - ScienceDirect

Plots of r⁴ vs. t (a) and r² vs. t (b) of Laves phases at two
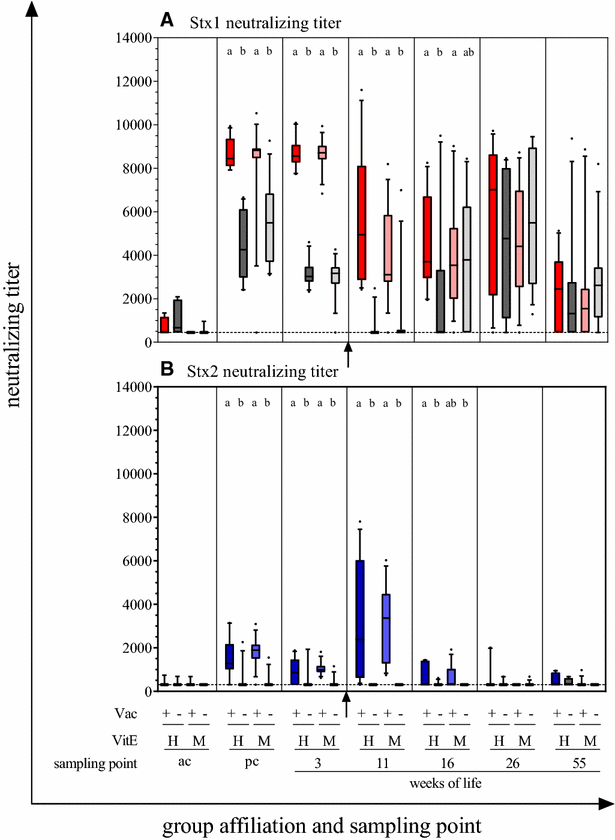
Decreased STEC shedding by cattle following passive and active vaccination based on recombinant Escherichia coli Shiga toxoids, Veterinary Research

PPT - Temperature dependence of the total, normal emissivity e n of selected materials PowerPoint Presentation - ID:3580734
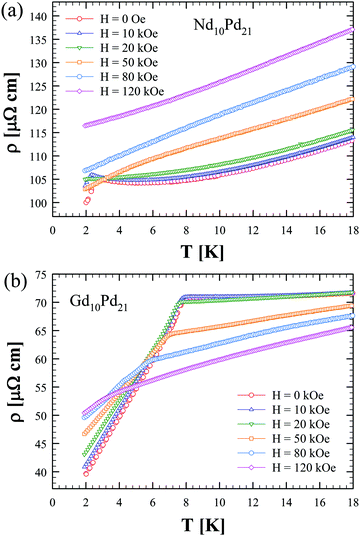
The R 10 Pd 21 compounds (R = Y, Pr, Nd, Sm, Gd–Lu). Crystal structure and magnetism of the 'RPd 2 ' phases - Journal of Materials Chemistry C (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C8TC00160J

Influence of Titanium Additions to Aluminum on the Microhardness Value and Electrochemical Behavior of Synthesized Aluminum-Titanium Alloy in Solutions of HCl and H3PO4
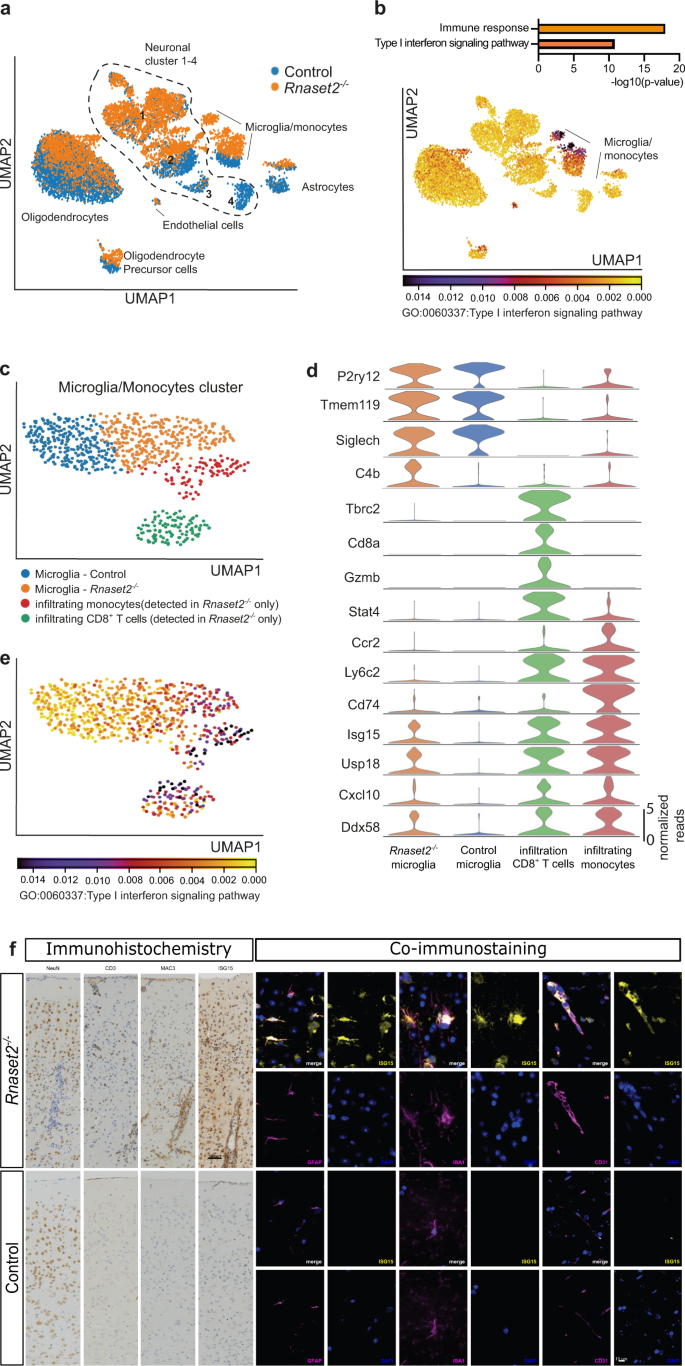
Interferon-driven brain phenotype in a mouse model of RNaseT2 deficient leukoencephalopathy

Chapter 2a: Pure Substances: Phase Change, Properties (updated 9/20/09)

Y. HAN, Professor (Associate), Tianjin University, Tianjin
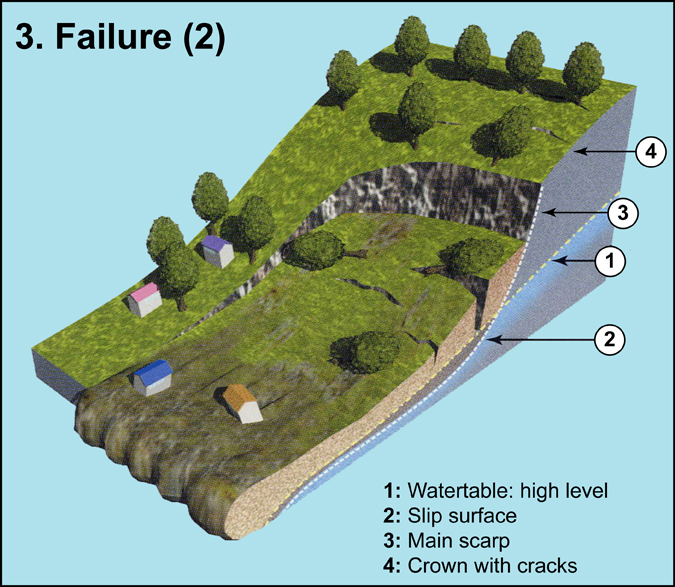
Landslides - BeSafeNet

The R 10 Pd 21 compounds (R = Y, Pr, Nd, Sm, Gd–Lu). Crystal structure and magnetism of the 'RPd 2 ' phases - Journal of Materials Chemistry C (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C8TC00160J